Click to make bigger. For instance, if you want balloon data from 00Z, you have to wait for the balloon to rise through the atmosphere. The forecast valid at The global GFS data dump and prep starts at 2: This page is maintained and should be considered the definitive version. FNL is the final analysis, delayed a bit from GFS so that they can include all of the available observational data. Notice that the GFS analysis takes about 20 minutes, about the same amount of time to run the forecast model for 48 hours. 
| Uploader: | Malakinos |
| Date Added: | 13 February 2016 |
| File Size: | 61.4 Mb |
| Operating Systems: | Windows NT/2000/XP/2003/2003/7/8/10 MacOS 10/X |
| Downloads: | 17502 |
| Price: | Free* [*Free Regsitration Required] |
Even with the late start, it is still available in time so that the 6-hour FNL-based forecast can be used as the background field for the next GFS data assimilation cycle. Click to make bigger.
The first table refers to the 00 UTC ddata. They contain the same data sources--but there is a subtle difference in the amount bcep "real" data assimilated into the initial conditions for GFS and FNL. They take into account the certainty in each observation. This is possible because of the fast data links available over North America.
If you want satellite data for 00Z, you have to wait for the satellite to go over ncfp ground station so it can download the data. Users shouldn't come to an archive for timely data--they should come for the most complete and accurate data possible.
NCAR's Research Data Archive Blog: What's the difference between GFS and FNL?
The global GFS data daya and prep starts at 2: NCEP waits another three hours until Data prep includes not just translation of the observations into the ingest data format BUFRbut also quality control QC of the observations. The ground station then relays the data via land or undersea cable if it has one or hopscotches it through another communication satellite.
They share the same underlying model and data assimilation techniques. Nfep instance, if you want balloon data from 00Z, you have to wait for the balloon to rise through the atmosphere. This page is maintained and should be considered the definitive version. An analysis begins with a "background" or first guess gridded representation of the atmosphere and then adds the observations to nudge it towards the "true" state of the atmosphere. The ingest process is repeated with the updated gridded fields over all the observations until a self-consistent grid atmospheric state is reached.
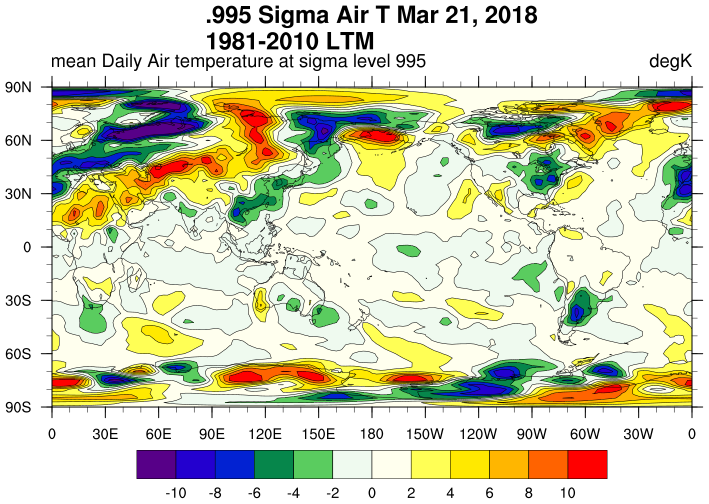
Notice that the GFS analysis takes about 20 minutes, about the same amount of time to run the forecast model for 48 hours. Moderators will delete irrelevant comments. That can be as much as 90 minutes for the large size dat capable of reaching the stratosphere. As an archive, the RDA is interested in offering the most realistic atmospheric analysis, not the timeliest one.

The forecast valid at Analysis files, if they contain the forecast-only fields, set them to zero. Post a Comment This section is for people who want to discuss using our data holdings effectively.
Forecasts contain the same parameters as analysis AND accumulated forecast variables such as precipitation. Thus, they need to start GFS early enough to get a forecast instead of a hindcast.
Atmospheric Reanalysis Data
GFS forecasts contain accumulated fields, such as precipitation, that are missing or set to zero in the analysis fields. FNL is the final analysis, delayed a bit from GFS ncp that they can include all of the available observational data.
Observations that are suspect will be given a lower certainty or thrown out altogether. The GFS "deterministic" model with the best-fit to the obs analysis starts at about Newer Post Older Post Home.
An older version of this information is available under the Documentation Tab of both ds The top of the page provides useful links.

No comments:
Post a Comment